What is a Good Credit Score?

Highlights:
- Credit scores are calculated using information in your credit reports.
- Credit scores generally range from 300 to 850.
- Different lenders have different criteria when it comes to granting credit.
It's an age-old question we receive, and to answer it requires that we start with the basics: What is the definition of a credit score, anyway?
Generally speaking, a credit score is a three-digit number ranging from 300 to 850. Credit scores are calculated using information in your credit report. Your payment history, the amount of debt you have and the length of your credit history are some of the factors that make up your credit scores.
There are many different credit scoring models, or ways of calculating credit scores. Credit scores are used by potential lenders and creditors, such as: banks, credit card companies or car dealerships, as one factor when deciding whether to offer you credit, like a loan or credit card. Credit scores help creditors determine how likely you are to pay back money they lend.
It's important to remember that everyone's financial and credit situation is different, and there's no credit score "magic number" that guarantees better loan rates and terms.
What are credit score ranges and what is a good credit score?
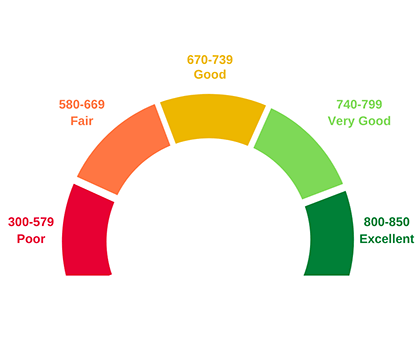
Credit score ranges vary depending on the scoring model. Higher credit scores mean you have demonstrated responsible credit behavior in the past, which may make potential lenders and creditors more confident when evaluating a request for credit. Most credit score ranges are similar to the following:
- 800 to 850: Excellent Credit Score
Individuals in this range are considered to be low-risk borrowers. They may have an easier time securing a loan than borrowers with lower scores. - 740 to 799: Very Good Credit Score
Individuals in this range have demonstrated a history of positive credit behavior and may have an easier time being approved for additional credit. - 670 to 739: Good Credit Score
Lenders generally view those with credit scores of 670 and up as acceptable or lower-risk borrowers. - 580 to 669: Fair Credit Score
Individuals in this category are often considered “subprime” borrowers. Lenders may consider them higher-risk, and they may have trouble qualifying for new credit. - 300 to 579: Poor Credit Score
Individuals in this range often have difficulty being approved for new credit. If you find yourself in the poor category, it's likely you'll need to take steps to improve your credit scores before you can secure any new credit.
Lenders use credit scores along with a variety of other types of information -- such as information you provide on the credit application (for example: income, how long you have lived at your residence, and other banking relationships you may have) in their loan evaluation process. Different lenders have different criteria when it comes to granting credit. That means the credit scores they accept may vary depending on their criteria.
Score providers, such as the three nationwide credit reporting agencies (NCRAs)—Equifax®, Experian® and TransUnion®—and companies like FICO® use different types of credit scoring models and may use different information to calculate credit scores. Therefore, credit scores may be different from each other. Not all creditors and lenders report to all credit score providers.
What is the average credit score?
As of January 2024 the average credit score in the United States was 701. While this is the average credit score, it falls in the Fair Range.
What factors impact your credit score?
Here are some tried and true behaviors to keep top of mind as you begin to establish—or maintain—responsible credit behaviors:
- Pay your bills on time, every time. This doesn't just include credit cards—late or missed payments on other accounts, such as cell phones, may be reported to the credit bureaus, which may impact your credit scores. If you're having trouble paying a bill, contact the lender immediately. Don't skip payments, even if you're disputing a bill.
- Pay off your debts as quickly as you can.
- Keep your credit card balance well below the limit. A higher balance compared to your credit limit may impact your credit score.
- Apply for credit sparingly. Applying for multiple credit accounts within a short time period may impact your credit score.
- Check your credit reports regularly. Request a free copy of your credit reports and check them to make sure your personal information is correct and there is no inaccurate or incomplete account information. Free online weekly credit reports are available at www.annualcreditreport.com. Remember: checking your credit reports or credit scores won't affect your credit scores.
You can also create a myEquifax™ account to get free Equifax credit reports each year. In addition, you can click “Get my free credit score” on your myEquifax dashboard to enroll in Equifax Core Credit™ for a free monthly Equifax credit report and a free monthly VantageScore® 3.0 credit score, based on Equifax data. A VantageScore is one of many types of credit scores.
If you find information you believe is inaccurate or incomplete, contact the lender or creditor. You can also file a dispute with the credit reporting agency (Equifax, Experian and/or TransUnion) about something wrong on your credit report. At Equifax, you can create a myEquifax account to file a dispute. Visit our dispute page to learn other ways you can submit a dispute.
Get your free credit score today!
We get it, credit scores are important. A monthly free credit score & Equifax credit report are available with Equifax Core CreditTM. No credit card required.



